| [1] 张志愿.口腔科学[M].6版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2004.
[2] 岳松龄.现代龋病学[M].6版.北京:北京医科大学中国协和医科大学联合出版社,1993.
[3] 章非敏,徐丽娜,孙卫斌,等.纳米增韧牙科复合树脂显微结构的研究[J].南京医科大学学报,2005,25(3):154-156.
[4] 陈旭,魏秀兰.FX玻璃离子水门汀修复乳磨牙的临床疗效[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2001,11(5):326-327.
[5] 张军,彭彬.不同类型玻璃离子水门汀氟离子体外释放的比较[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2008,18(1):28-30.
[6] Grobler SR,Rossouw RJ,Van Wyk Kotze TJ. A comparison of fluoride release from various dental materials.J Dent.1998; 26(3): 259-265.
[7] Freedman R,Diefenderfer KE.Effects of daily fluoride exposures on fluoride release by glass ionomer-based restoratives. Oper Dent.2003;28(2):178-185.
[8] 彭儒,罗廉明.磷矿选矿[M].武汉:武汉测绘科技大学出版社, 1992:14-16.
[9] 李世普.生物医用材料导论[M].武汉:武汉工业大学出版社,2000: 48-49,120-123.
[10] 张士成,李世普,陈芳.磷灰石超微粉对癌细胞作用的初步研究[J].武汉工业大学学报,1996,18(1):5-8.
[11] Mendez-Gonzalez M,Cauich-Rodriguez JV.Preparation of porous hydroxyapatite tablets and porous hydroxyapatite coat- ing for orthopaedic use.Key Eng Mater.2001;192: 259-261.
[12] 郑岳华,侯小妹,杨兆雄.多孔羟基磷灰石生物陶瓷的进展[J].硅酸盐通报,1995,14(3):20-24.
[13] International Organization for Standardization. ISO 7489. Dental glass polyalkenoate cements. Genebra; 1986.
[14] Mjor IA,Toffenetti F.Secondary caries: a literature review with case reports.Quintessence Int.2000;31(3):165-179.
[15] 莫思溯,刘正,李鸣宇.继发龋的诊断和预防[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2006,16(1):55-58.
[16] 吴清柱.三种牙体充填材料边缘封闭性的实验研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2005,19(1):82-83.
[17] Sallsten G,Thoren J,Barregard L,et al.Long-term use of nicotine chewing gum and mercury exposure from dental amalgam fillings.Dent Res.1996;75:594-598.
[18] Wilson AD,Kent BE.A new translucent cement for dentistry.Br Dent J.1972;15:132-133.
[19] Christensen GJ.Why is glass ionomer cement so popular? J Am Dent Assoc.1994;125(9): 1257-1258.
[20] 梁桂香.三种方法修复楔形缺损疗效对比[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2004,14(3): 450.
[21] Heintze SD,Cavalleri A,Forjanic M,et al.Wear of ceramic and antagonist-a systematic evaluation of influencing factors in vitro.Dent Mater. 2008;2(44):433-449.
[22] 张之南.血液病诊断及疗效标准[M].2版.北京:北京科技出版社, 1998:168-236.
[23] Grimwade D,Walker H,Oliver F,et al.The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 Trial.Blood.1998;92(7): 2322-2333.
[24] 史宇,刘鲁川,温秀杰,等.几种银汞合金替代材料微渗漏的体外实验研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2004,26(16):1496-1498.
[25] 周瑞庆,蒋丽萍,钱家生,等.三种黏接材料的体外微渗漏研究[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版,2008,28(10):254-1257. |

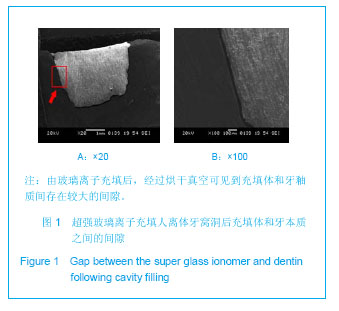
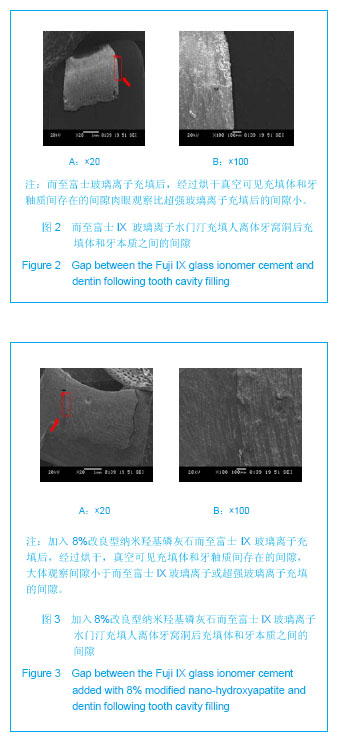
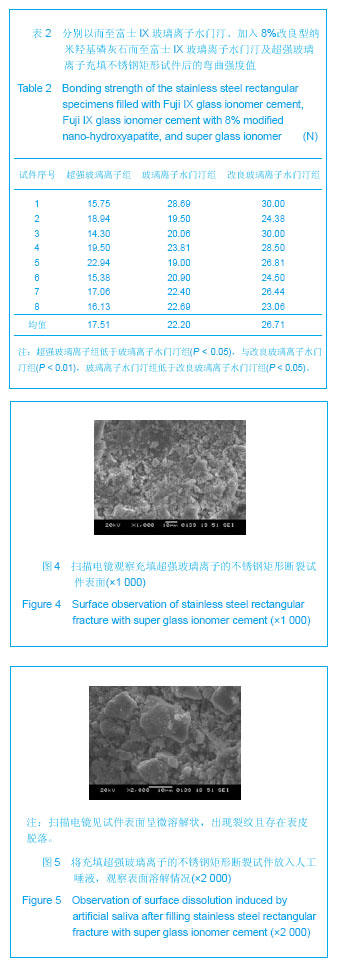


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)